- Visibility 42 Views
- Downloads 5 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.jds.2024.032
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Taming the vertical growth of mandible in a growing patient with skeletal open bite: A case report
- Author Details:
-
Puneet Kumar
-
Shubhangi Jain *
-
Prachi Mehra
-
Prachi Saraswat
-
Pranjal Pratim Kashyap Paul
Introduction
Patients with skeletal open bite generally present with downward and backward rotation of the mandible and vertical overgrowth of the maxilla. The condition presents a challenge to treat as well as maintain post treatment stability. [1] An excessive vertical growth caused by skeletal disharmonies, a lack of muscular balance, habits like digit sucking, abnormal tongue function, airway obstruction, or iatrogenic treatments can all contribute to the development of an anterior open bite.[2] A skeletal open bite correction requires procedures designed to intrude the posterior teeth or prevent the molar extrusion to control the anterior facial height. Some common appliances utilized for producing these tooth movements can be high pull headgears, lingual arches, and posterior bite blocks to control molar extrusion.[3] The advent of mini-implants and mini-plates also expands the envelope of possible molar intrusion, previously not possible without orthognathic surgery. Titanium miniplates implanted in the buccal cortical bone in the apical regions of the first and second molars have been shown to produce as much as 3 to 5 mm of molar intrusion.[3]
Treatment of patients with a hyperdivergent skeletal phenotype must be performed early to be successful. Since facial growth Patterns are established early in development, hyperdivergent phenotype untreated until the permanent dentition stage of development is a lost opportunity for growth modification. Furthermore, early treatment can improve a child’s self-esteem by improving appearance. [4]
Severe anterior open bites may warrant the use of multiple modalities for effective treatment results. The current case report highlights the treatment of skeletal open bite of a growing individual treated with high pull headgear and palatal mini-implants.
Case Report
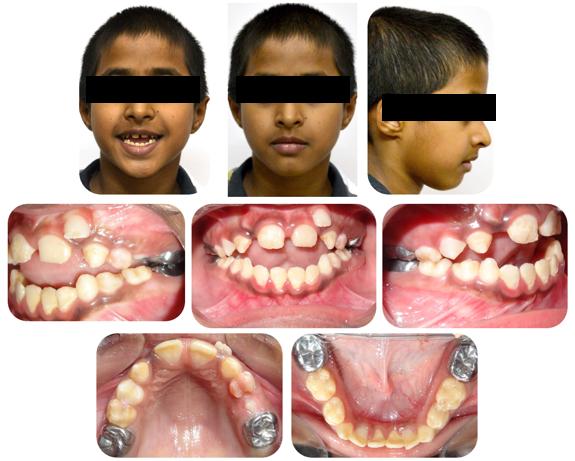
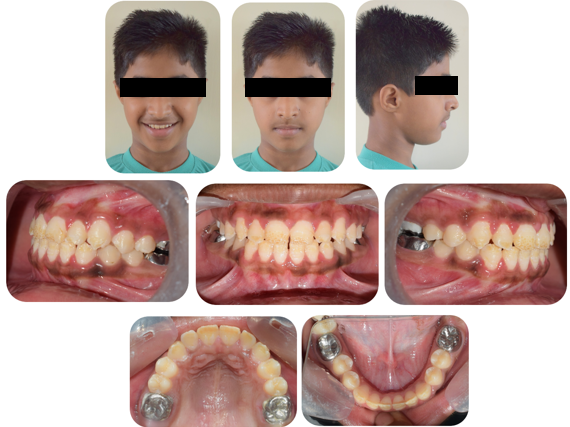
A 9 year old male reported to the Department of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopaedics, I.T.S Dental College, Muradnagar, Ghaziabad with the chief complaint of inability to bite from the front teeth. Extraoral examination revealed a bilaterally symmetrical face, incompetent lips , convex facial profile, skeletal class I jaw relationship with a vertical growth pattern. The patient also showed an increased lower anterior facial height and reduced upper incisor exposure. Intraoral examination showed that the patient was in early mixed dentition phase with end on molar relationship on both the sides and an anterior open bite of 6 mm. The frontal intraoral photograph revealed that the tongue interposed in between the upper and lower anterior teeth preventing their eruption.([Figure 1])
The patient also presented with enamel hypoplasia in the incisors and molars. The maxillary and mandibular molars had been restored with a stainless steel crown.
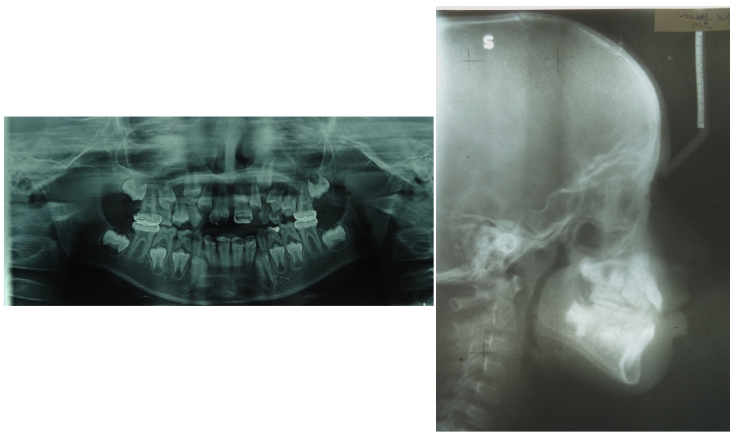
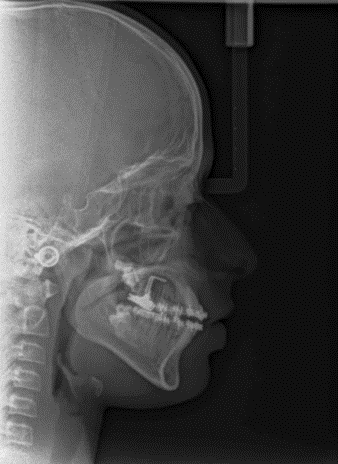
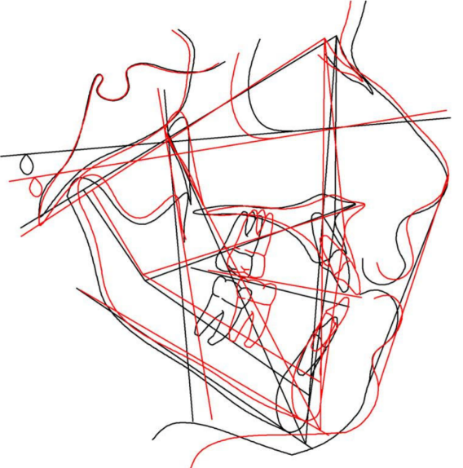
The lateral cephalogram confirmed a class I skeletal pattern with a vertical growth pattern and increased lower anterior facial height. There was a normal position of upper and slightly protruded lower incisors.([Figure 2])([Table 1])
Treatment objectives were to close the open bite while reducing the lower anterior facial height, correct the overjet and crowding, and obtain an ideal occlusion, while improving the smile esthetics.
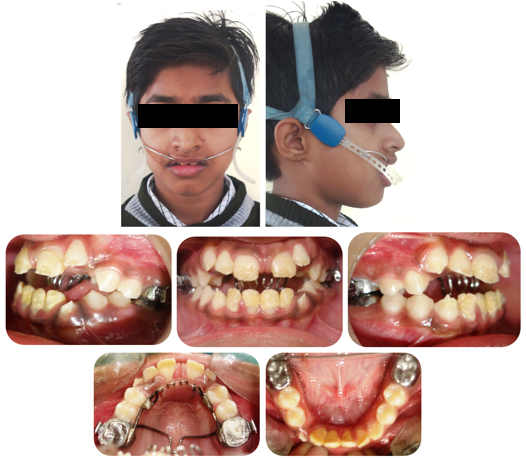
Since the patient was in early growth phase, the first phase of treatment plan included intrusion of molars with a high pull headgear for 10-12 hours with an activation force of 250-300gms. Additionally an intraoral appliance consisting of transpalatal arch placed away from palate and a modified Nance palatal arch with tongue cribs to control the tongue posture and vertical position of maxillary molars.([Figure 3]) The headgear with the intra-oral soldered appliance reduced the open bite substantially in a period of 9 months. The headgear also restricted the forward movement of the maxillary molar to allow for a class I molar relationship to develop through growth.
The second phase of treatment involved fixed orthodontic appliance therapy with placement of para sagittal TADs (1.5mmx8mm) and transpalatal arch for active molar intrusion. The fixed appliance allowed for alignment of the maxillary and mandibular arch and incisor extrusion and improve incisor exposure.([Figure 4])
An e chain from the TADs to the transpalatal arch provided active molar intrusion..
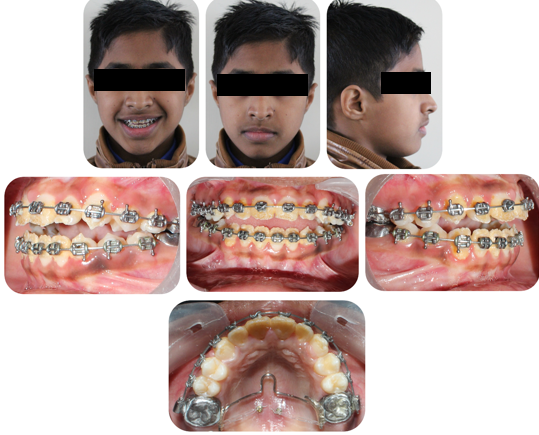
At the end of the treatment patient the anterior open bite was eliminated through slight posterior intrusion, incisor extrusion and autorotation of the growing mandible. The incisor exposure was improved and the patient had class I molar and canine relationship with well aligned arches.([Figure 5])
The cephalometric values revealed a reduction in the mandibular plane angle by 5°, reduction in lower anterior facial height by 4mm, mild proclination of the maxillary and mandibular incisors, maintenance of position of the incisors, reduction in the overbite, extrusion of upper incisor, and improvement of facial profile. ([Figure 6], [Figure 7]),([Table 1])
|
Parameter |
Pre treatment |
Post treatment |
|
SNA |
76° |
80° |
|
SNB |
72° |
76° |
|
ANB |
4° |
4° |
|
SN-GoGn |
45° |
40° |
|
U1-NA |
3mm |
2mm |
|
L1-NB |
6mm |
7mm |
|
U1-SN |
97.5° |
108° |
|
U1-APog |
6mm |
6mm |
|
L1-Apog |
4mm |
3.5mm |
|
N Perp -A |
-5mm |
-3.3mm |
|
N Perp -Pog |
-17mm |
-17mm |
|
Max Length |
70mm |
73mm |
|
Mand Length |
91mm |
93mm |
|
LAFH |
67mm |
63mm |
|
E Line |
-2.6mm/1.3mm |
-2mm/-0.4mm |
|
Wits Appraisal |
-4mm |
0.1mm |
Discussion
The present case highlights the correction of skeletal open bite in a growing patient using orthopaedic appliance followed by temporary anchorage device. The patient was diagnosed with skeletal open bite due to the excess clockwise rotation of the mandible and diverging jaw bases with an increased lower anterior face height. The high pull headgear applied forces in the superior and distal direction to restrain vertical eruption and mesial movement of the molar. Several studies have investigated the effect of high pull headgear on the vertical molar position and mandibular plane angle. Firouz et al [5] examined the skeletal and dental effects of a high pull headgear vs a control group. He observed that the molars were intruded 0.54 mm in the high-pull headgear group and extruded 0.42 mm in the control group. Fotis et al [6] also studied the effect of high pull headgear where he found that the SN-MP angle remained relatively constant only increasing minimally (0.4°) and the distance from a point on maxillary first molar to SN was reduced 0.5 mm showing that the vertical development of the maxillary molar was restricted.
Headgear provided good vertical control and helped in substantial reduction of overjet, however such orthopaedic appliances achieve correction primarily through extrusion of incisors or by preventing passive eruption of posterior teeth. [7]
Since the patient had a severe skeletal open bite and a massive open bite, further intervention was required to completely close the bite.
The advent of Skeletal anchorage using mini-implant anchorage and miniplates have enabled the orthodontists to perform difficult tooth movements without surgery. Previous studies by Baek et al, [8] Deguchi et al, [9] Lee et al [10] and Xun et al [11] have highlighted reduction in mandibular plane angulation, overbite, and maxillary first molar height using TADs.
There was mild intrusion of the maxillary molar and excellent vertical control observed in the current case report.
Since the patient was in mixed dentition phase, the TADs could not be placed in the buccal alveolus between second premolar and first molar. The para sagittal region provided the best quality of bone in relation to the density thus was the chosen site for the placement of TADs.
Fixed orthodontic appliance with posterior vertical control allowed for extrusion in the incisors which was favorable in the current case due to insufficient incisor exposure.
The forward tongue posture was identified in the patient, thus tongue cribs on a modified Nance appliance contributed to reduction of overbite in the first phase of treatment.
The Transpalatal arch allowed for anchorage to first molars in transverse direction and assisted in molar intrusion as it was kept away from palate.
Conclusion
The case presented in the case report was successfully treated by high pull headgear followed by TADs. This approach can be useful in treating young growing individuals where the maxillary growth can be restricted followed by skeletal anchorage which can result in active molar intrusion whilst providing stable results
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- JY Hsu, JH Cheng, SW Feng, PC Lai, N Yoshida, PC Chiang. Strategic treatment planning for anterior open bite: A comprehensive approach. J Dent Sci 2024. [Google Scholar]
- DE Rodríguez Sánchez, JR Hernández Gómez, GP Cotter, JA Rodríguez Chávez, C Orozco Varela. Anterior open bite correction in a skeletal class II patient: Case report. Rev Mex Ortod 2016. [Google Scholar]
- RA Beane. Nonsurgical management of the anterior open bite: a review of the options. Semin Orthod 1999. [Google Scholar]
- JD English. Early treatment of skeletal open bite malocclusions. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2002. [Google Scholar]
- M Firouz, J Zernik, R Nanda. Dental and orthopedic effects of high-pull headgear in treatment of Class II, division 1 malocclusion. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 1992. [Google Scholar]
- V Fotis, B Melsen, S Williams, H Droschl. Vertical control as an important ingredient in the treatment of severe sagittal discrepancies. Am J Orthod 1984. [Google Scholar]
- N Erverdi, A Keles, R Nanda. The use of skeletal anchorage in open bite treatment: a cephalometric evaluation. Angle Orthod 2004. [Google Scholar]
- MS Baek, YJ Choi, HS Yu, KJ Lee, K Kwak, YC Park. Long-term stability of anterior open-bite treatment by intrusion of maxillary posterior teeth. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Ortho 2010. [Google Scholar]
- T Deguchi, H Kurosaka, H Oikawa. Comparison of orthodontic treatment outcomes in adults with skeletal open bite between conventional edgewise treatment and implant-anchored orthodontics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2011. [Google Scholar]
- H Lee, Y Park. Treatment and posttreatment changes following intrusion of maxillary posterior teeth with miniscrew implants for open bite correction. Korean J Orthod 2008. [Google Scholar]
- C Xun, X Zeng, X Wang. Microscrew anchorage in skeletal anterior open-bite treatment. Angle Orthod 2007. [Google Scholar]
